In complex systems, failures are inevitable; preventing failures is impossible. There are, however, multiple ways of responding to failures. For example, ANTIFRAGILITY is a qualification of complex adaptive systems that increase in capability, resilience, or robustness as a result of stress or failure.
It is contrasted with:
- fragility (failing)
- resilience (recovering from failure)
- and robustness (resisting failure)
A fragile system is damaged—possibly catastrophically
A robust system is largely unaffected, retaining much or all of its prior strength
Some systems actually gain strength, a property which has recently been termed antifragility.
Traditional perspectives of Digital Organization implicitly assume fragility, limiting their validity and resulting in surprise, and assume a specific end state rather than an overall condition of the system as a goal.
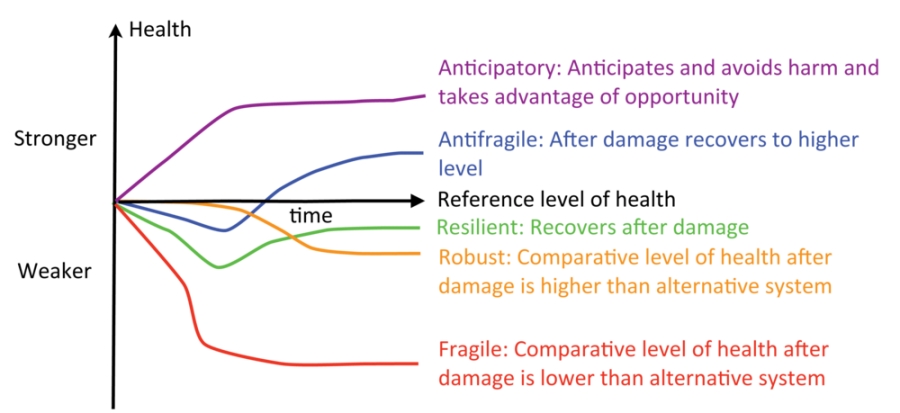
We can combine the response to damage with the ability to anticipate (to act to avoid damage or exploit opportunities) creating a more complete characterization of system properties as shown in figure.
Characterization of the changes in system health when subject to external stresses.
System properties can include:
- the ability to anticipate, resulting in avoidance of harm or exploitation of opportunities (anticipatory, purple),
- the ability to recover from damage to a higher level of health than before (antifragile, blue),
- the ability to recover from damage (resilient, green),
- the ability to withstand damage (robust, orange), and
- breaking under stress (fragile, red).